React 핵심 패턴

# JSX 컴포넌트 구조
React 프로젝트에서 단일 .jsx 파일을 컴포넌트(Component)라고 부릅니다.
다음과 같은 기본 구조를 가지며, 컴포넌트 이름은 일반적으로 파스칼 케이스로 작성합니다.
12345export default function 컴포넌트이름() { return ( // 템플릿(Template) ) }
React 17버전부터는 타입을 사용할 때 컴포넌트 상단에 import React from ‘react’ 코드를 명시할 필요가 없습니다.
단, 일부 프로젝트의 개발 도구나 환경에 따라 해당 코드 명시가 필요할 수도 있습니다.
# JSX fragment
React 컴포넌트는 여러 최상위 요소를 지정할 수 없습니다.
다음과 같이 하나의 최상위 요소(<div>)만 지정해야 합니다.
123456789export default function App() { return ( <div> <header>HEADER</header> <main>MAIN</main> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </div> ) }
하지만 이것은 다음과 같이 요소들을 이중으로 묶는 불필요한 요소가 되기도 합니다.
123456789<body> <div id="root"> <div> <!-- 불필요한 div 요소 --> <header>HEADER</header> <main>MAIN</main> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </div> </div> </body>
컴포넌트의 최상위 요소로 JSX fragment(<></>)를 사용하면, 별도의 요소를 생성하지 않고 여러 요소를 묶어 하나의 자식 요소처럼 출력할 수 있습니다.
123456789export default function App() { return ( <> <header>HEADER</header> <main>MAIN</main> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </> ) }
이제 다음과 같이 출력합니다.
12345678<body> <div id="root"> <!-- 중간 div 요소 없음 --> <header>HEADER</header> <main>MAIN</main> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </div> </body>
만약 JSX fragment에 속성을 지정해야 하는 경우, 명시적으로 <Fragment> 컴포넌트를 사용해야 합니다.
1234567891011import { Fragment } from 'react' export default function App() { return ( <Fragment key={'123'}> <header>HEADER</header> <main>MAIN</main> <footer>FOOTER</footer> </Fragment> ) }
# 데이터 보간
컴포넌트 템플릿(Template)에서 {} 기호를 사용해 데이터를 쉽게 출력할 수 있습니다.
이를 보간법(Interpolation)이라고 부릅니다.
1234567export default function App() { const name = 'ParkYoungWoong' return ( <h1>Hello, {name}!</h1> ) }
템플릿의 {} 기호 사이에서 간단한 표현식(Expression)을 사용할 수 있습니다.
123456789101112export default function App() { const count = 1 const getFullName = (firstName, lastName) => `${firstName} ${lastName}` return ( <> <h2>{count + 7}</h2> <h2>{getFullName('YoungWoong', 'Park')}</h2> </> ) }
# 반응형 데이터
React에서 데이터가 변경될 때 그것이 연결된 화면(View)도 같이 변경되는 것을 데이터의 반응성(Reactivity)이라고 합니다.
그리고 그 데이터를 반응형 데이터(Reactive state)라고 부르며, 줄여서 반응형이라고도 합니다.
다음과 같이 useState 함수를 사용해 반응형 데이터를 만들 수 있습니다.
1234567import { useState } from 'react' // 반응형 데이터 선언 const [데이터이름, 데이터변경함수] = useState(기본값) // 반응형 데이터 변경 데이터변경함수(변경할값)
12345678910111213141516import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) const increment = () => { setCount(count + 1) } return ( <> <p>현재 카운트: {count}</p> <button onClick={increment}>카운트 증가</button> </> ) }
# 이벤트 핸들링
템플릿에서 on 키워드와 이벤트 이름을 조합해 요소의 속성으로 작성하고 실행할 함수를 연결합니다.on 키워드와 조합된 이름은 onClick, onKeyDown과 같이 카멜 케이스로 작성해야 합니다.
123456<div on이벤트이름={실행할함수}></div> // 예시 <div onClick={handler}></div> <div onChange={handler}></div> <div onKeyDown={handler}></div>
12345678910111213141516import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) const increment = () => { setCount(count + 1) } return ( <> <p>현재 카운트: {count}</p> <button onClick={increment}>카운트 증가</button> </> ) }
# HTML Class 바인딩
class는 자바스크립트에서 예약어(Reserved words)이므로 JSX 템플릿에서는 HTML 속성(Attribute)으로 class 대신 className을 사용해야 합니다.
12345678910111213import { useState } from 'react' import './App.css' export default function App() { const [active, setActive] = useState(false) return ( <> <h1 className={`btn ${active ? 'active' : ''}`}>Hello world!</h1> <button onClick={() => setActive(!active)}>Toggle class name!</button> </> ) }
123.active { color: red; }
여러 클래스 이름을 데이터 여부로 출력하는 경우, 다음과 같이 불린 데이터를 기반으로 클래스 이름이 적용될 수 있도록 코드를 작성할 수도 있습니다.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435import { useState } from 'react' import './App.css' export default function App() { const [btn, setBtn] = useState(false) const [active, setActive] = useState(false) const [size, setSize] = useState(false) const getClassNames = names => Object.keys(names) .filter(name => names[name]) .join(' ') const classNames = getClassNames({ btn, active, size }) return ( <> <h1 className={classNames}>Hello world!</h1> <button onClick={() => setBtn(!btn)}> Toggle 'btn' </button> <button onClick={() => setActive(!active)}> Toggle 'active' </button> <button onClick={() => setSize(!size)}> Toggle 'size' </button> </> ) }
123456789.btn { border: 4px solid; } .active { color: red; } .size { font-size: 16px; }
# HTML Style 바인딩
style 속성으로 인라인 스타일을 적용할 수 있습니다.
객체 데이터로 작성할 수 있으며, 자바스크립트 표기법에 맞게 낙타 표기법(camelCase)로 CSS 속성(Properties)을 작성해야 합니다.
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [size, setSize] = useState(16) const styles = { fontSize: `${size}px`, // 동적(dynamic) 값은 반응형 데이터로 관리합니다! fontWeight: '700' // 정적(static) 값은 별도의 CSS 파일로 관리하는 게 좋습니다. } return ( <> <button onClick={() => setSize(size + 3)}> Size up! </button> <button onClick={() => setSize(size - 3)}> Size down! </button> <p style={styles}> Hello world! </p> </> ) }
# 조건부 렌더링
# 논리 연산자
조건에 따라 템플릿(HTML)을 출력하거나 출력하지 않습니다.
123456789101112131415import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [message, setMessage] = useState('') return ( <> <input value={message} onChange={e => setMessage(e.target.value)} /> {message.trim() && <div>입력된 내용이 있어요~</div>} </> ) }
# 삼항 연산자
조건에 따라 각자 다른 템플릿을 출력합니다.
123456789101112131415161718import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [isActive, setIsActive] = useState(false) const toggle = () => { setIsActive(!isActive) } return ( <> {isActive ? <h1>활성화 - {String(isActive)}</h1> : <h1>비활성화 - {String(isActive)}</h1>} <button onClick={toggle}>토글</button> </> ) }
# 더 복잡한 조건
조건에 따라 출력할 템플릿이 2개 이상인 경우, 표현식이 아닌 구문(Statement)을 템플릿에 직접 사용할 수 없기 때문에, 다음과 같이 별도 함수로 만들어 사용할 수 있습니다.
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [state, setState] = useState('') const renderStateMessage = () => { if (state === 'loading') { return <h2>로딩 중입니다.</h2> } else if (state === 'success') { return <h2>성공적으로 완료되었습니다.</h2> } else { return <h2>대기 중입니다.</h2> } } return ( <> <button onClick={() => setState('loading')}> 로딩! </button> <button onClick={() => setState('success')}> 성공! </button> {renderStateMessage()} </> ) }
# 리스트 렌더링
데이터를 기반으로 목록을 출력할 수 있습니다.
데이터의 변경사항이 있을 때 React가 반응성(Reactivity)을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있도록, 반복되는 각 요소에 key 속성과 함께 항목별 고유한 값을 작성해야 합니다.key 속성의 고유한 값은 일반적으로 문자나 숫자 데이터를 권장합니다.
1234567891011121314export default function App() { const fruits = ['사과', '바나나', '체리'] const renderFruits = fruits.map((fruit, index) => ( <li key={index}>{fruit}</li> )) return ( <> <h1>과일 리스트</h1> <ul>{renderFruits}</ul> </> ) }
별도의 함수를 만들지 않고 다음과 같이 템플릿에 직접 작성할 수도 있습니다.
1234567891011121314export default function App() { const fruits = ['사과', '바나나', '체리'] return ( <> <h1>과일 리스트</h1> <ul> {fruits.map((fruit, index) => ( <li key={index}>{fruit}</li> ))} </ul> </> ) }
# 계산된 데이터
useMemo 함수를 사용해 데이터가 변경될 때 그것을 기반으로 자동 계산되어(Computed) 업데이트되는 별도의 데이터를 만들 수 있습니다.
기반 데이터는 반응형이어야 합니다!
1234import { useMemo } from 'react' // 계산된 데이터 선언 const 계산된데이터 = useMemo(() => 새로운값, [기반데이터])
123456789101112131415import { useState, useMemo } from 'react' export default function App() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) const double = useMemo(() => count * 2, [count]) return ( <> <h1>count: {count}</h1> <h2>double: {double}</h2> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>증가</button> </> ) }
# 데이터 감시
useEffect 함수를 사용해 데이터가 변경될 때 그것을 감시(Watch)하여 자동으로 실행되는 함수(콜백)를 만들 수 있습니다.
감시할 데이터는 반응형이어야 합니다!
1234import { useEffect } from 'react' // 데이터 감시 선언 useEffect(실행할함수, [감시할데이터])
12345678910111213141516import { useState, useEffect } from 'react' export default function App() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0) useEffect(() => { console.log('count 값이 변경되었습니다:', count) }, [count]) return ( <> <h1>카운트: {count}</h1> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>증가</button> </> ) }
만약 useEffect 함수 콜백이 최초 렌더링 시 2번 연속으로 실행되는 경우, <React.StrictMode>를 사용하지 않는 것을 고려하세요.
이것은 프로젝트의 문제를 감지하고 경고해주는 도구로 의도적으로 2번의 렌더링을 사용할 수 있습니다.
단순히 개발 모드에서만 활성화되고 빌드 결과(제품)에는 영향을 끼치지 않으니 제거해도 좋습니다.
123456789101112131415import React from 'react' import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client' import App from '~/App' // ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render( // <React.StrictMode> // <App /> // </React.StrictMode> // ) ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render( <> <App /> </> )
# 양식 입력 바인딩
input이나 textarea 같은 양식(Form) 요소와 React의 반응형 데이터를 연결하는 여러 패턴의 예제를 소개합니다.
# 텍스트
123456789101112131415import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [text, setText] = useState('') return ( <> <input value={text} onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)} /> <h2>{text}</h2> </> ) }
# 여러 줄 텍스트
123456789101112131415import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [text, setText] = useState('') return ( <> <textarea value={text} onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)} /> <pre>{text}</pre> </> ) }
# 수정 가능 요소
일반 요소는 contenteditable 속성을 통해, 수정 가능 요소로 만들어 텍스트를 수정할 수 있습니다.
1<div contenteditable>Content!</div>
하지만 React에서 이 속성을 사용하면, 가상 DOM 충돌, 이벤트 점프 등의 문제가 발생할 수 있기 때문에, 일반적인 문제가 대부분 해결된 react-contenteditable 라이브러리를 사용하는 것을 추천합니다.
1npm i react-contenteditable
<div>, <br/> 같은 요소를 통해 줄바꿈 처리를 하므로, 입력된 값이 없으면 내용을 비웁니다.placeholder 속성 대신 aria-placeholder 속성을 사용해 힌트를 제공할 수 있습니다.(CSS 코드를 같이 제공해야 합니다)
1234567891011121314151617181920212223import { useRef, useState } from 'react' import ContentEditable from 'react-contenteditable' export default function App() { const ref = useRef<HTMLElement>(null) const [text, setText] = useState('') function onChange() { if (ref.current && !ref.current.textContent) { setText('') } } return ( <> <ContentEditable innerRef={ref} html={text} onChange={onChange} aria-placeholder="텍스트를 입력하세요!" /> </> ) }
1234[contenteditable]:empty::before { content: attr(aria-placeholder); color: #aaa; }
# 단일 체크박스
12345678910111213141516171819import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [checked, setChecked] = useState(false) return ( <> <label> <input type="checkbox" checked={checked} onChange={(e) => setChecked(e.target.checked)} /> 동의합니다. </label> <h2>동의 여부: {checked ? '예' : '아니오'}</h2> </> ) }
# 다중 체크박스
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [checkedItems, setCheckedItems] = useState([]) const handleCheckboxChange = event => { const { value, checked } = event.target checked ? setCheckedItems([...checkedItems, value]) // 체크한 경우 : setCheckedItems(checkedItems.filter((item) => item !== value)) // 체크 해제한 경우 } return ( <> <p>좋아하는 음식을 모두 골라보세요~</p> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="사과" checked={checkedItems.includes('사과')} onChange={handleCheckboxChange} /> 사과 </label> <br /> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="바나나" checked={checkedItems.includes('바나나')} onChange={handleCheckboxChange} /> 바나나 </label> <br /> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="체리" checked={checkedItems.includes('체리')} onChange={handleCheckboxChange} /> 체리 </label> <br /> <h2>{checkedItems.join(', ')}</h2> </> ) }
# 라디오 버튼
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [text, setText] = useState('') return ( <> <label> <input type="radio" value="사과" checked={text === '사과'} onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)} /> 사과 </label> <label> <input type="radio" value="바나나" checked={text === '바나나'} onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)} /> 바나나 </label> <h2>{text}</h2> </> ) }
# 단일 선택
12345678910111213141516171819import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [selected, setSelected] = useState('') return ( <> <select value={selected} onChange={e => setSelected(e.target.value)}> <option value="">선택하세요</option> <option>사과</option> <option>바나나</option> <option>체리</option> </select> <h2>{selected}</h2> </> ) }
# 다중 선택
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233import { useState } from 'react' export default function App() { const [selected, setSelected] = useState([]) const handleChange = event => { const { options } = event.target const newSelected = [] Array.from(options).forEach((option) => { if (option.selected) { newSelected.push(option.value) } }) setSelected(newSelected) } return ( <> <select multiple value={selected} onChange={handleChange} style={{ width: '100px' }}> <option>사과</option> <option>바나나</option> <option>체리</option> <option>오렌지</option> <option>딸기</option> </select> <h2>{selected.join(', ')}</h2> </> ) }
# 템플릿(요소) 참조
document.querySelector를 통해 요소를 검색하지 않고, 대신 useRef 함수를 사용해 템플릿(요소)을 바로 참조하도록 만들 수 있습니다.
기본값(Default value)은 요소를 찾지 못한 결과를 의미하는 null을 사용합니다.
참조 요소는 다음 예제의 inputRef.current와 같이 current 속성으로 확인합니다.
123456789101112131415import { useRef } from 'react' export default function App() { const inputRef = useRef(null) return ( <> <input type="text" ref={inputRef} /> <button onClick={() => inputRef.current.focus()}>포커스!</button> </> ) }
# 컴포넌트
# 생명주기 훅
input 요소가 화면에 보이면 자동으로 포커스(Focus) 하기 위해 다음 예제와 같이 작성하면 에러가 발생합니다.
이것은 React 컴포넌트의 자바스크립트 코드가 동작하는 시점(Created)과 템플릿이 화면에 렌더링 되는 시점(Mounted)이 다르기 때문입니다.
123456789101112131415161718import { useRef } from 'react' export default function App() { const inputRef = useRef(null) // input 요소에 포커스! // Error - cannot read properties of null (reading 'focus') inputRef.current.focus() return ( <> <input type="text" ref={inputRef} /> </> ) }
다음과 같이 useEffect 함수를 사용하면, 템플릿이 화면에 렌더링 된 후 함수를 실행할 수 있습니다.useEffect 함수는 데이터를 감시할 때도 사용하지만, 이렇게 ‘화면 준비 후’에 실행될 함수를 작성할 때도 사용합니다.
단, 감시할 데이터가 없기 때문에 두 번째 인수는 빈(Empty) 배열입니다.
123import { useEffect } from 'react' useEffect(실행할함수, [])
이제 잘 동작합니다!
12345678910111213141516171819import { useRef, useEffect } from 'react' export default function App() { const inputRef = useRef(null) // 화면이 준비되면, input 요소에 포커스! useEffect(() => { inputRef.current.focus() }, []) return ( <div> <input type="text" ref={inputRef} /> </div> ) }
만약 다음과 같이 useEffect 함수의 두 번째 인수로 배열을 전달하지 않으면, 반응형 데이터 갱신 등의 영향으로 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링 될 때마다 콜백이 실행됩니다.
일반적인 경우에 추천하는 방법은 아닙니다.
1234// 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링(Rerendering) 될 때마다 콜백이 실행 useEffect(() => { console.log('count 값이 변경되었습니다:') })
# 부모와 자식 컴포넌트
컴포넌트는 다른 컴포넌트를 가져와서 사용할 수 있습니다.
가져온 컴포넌트는 나의 자식 컴포넌트라고 부르며, 나는 자식의 부모 컴포넌트라고 부릅니다.
다음 예제에서 TextField.jsx는 App.jsx의 자식 컴포넌트이고, App.jsx는 TextField.jsx의 부모 컴포넌트입니다.
HTML 요소의 부모/자식 관계 개념과 같습니다.
1234567export default function TextField() { return ( <> <input type="text" /> </> ) }
Vite 프로젝트에서는 가져오기 경로의 .jsx 컴포넌트 확장자를 생략할 수 있습니다.
1234567891011import TextField from './components/TextField' export default function App() { return ( <> <TextField /> <TextField /> <TextField /> </> ) }
# Props
부모 컴포넌트에서 자식 컴포넌트로 데이터(반응형 데이터, 함수 등)를 전달할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 전달하는 데이터 혹은 그 속성을 Prop이라고 부릅니다.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223export default function TextField({ label = '', hint = '', value, onChange }) { return ( <div style={{ marginBottom: '10px' }}> <label> {label && `${label}::`} <input type="text" value={value} onChange={e => onChange(e.target.value)} /> </label> {hint && ( <div style={{ marginTop: '4px', fontSize: '11px' }}> {hint} </div> )} </div> ) }
다음과 같이 컴포넌트(<TextField>)를 사용할 때, HTML 속성(Attribute)처럼 작성해 데이터를 전달합니다.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132import { useState } from 'react' import TextField from '@/components/TextField' export default function App() { const [name, setName] = useState('') const [age, setAge] = useState('') const [email, setEmail] = useState('') return ( <> <TextField name="이름" hint="한글 이름을 입력해야 합니다." value={name} onChange={setName} /> <TextField name="나이" hint="만 나이를 입력해야 합니다." value={age} onChange={setAge} /> <TextField name="이메일" value={email} onChange={setEmail} /> <div> 이름은 {name}이고 나이는 {age}세이고 이메일은 {email}입니다! </div> </> ) }
# 폴스루 속성
컴포넌트에서 Props로 정의하지 않았지만, 컴포넌트를 사용할 때 작성한 속성을 폴스루 속성(Fallthrough props)이라고 부릅니다.
12345678910111213141516171819202122import { useState } from 'react' import TextField from '@/components/TextField' export default function App() { const [email, setEmail] = useState('') return ( <> <TextField label="이메일" value={email} onChange={setEmail} placeholder="이메일을 입력해주세요." name="Email" minlength="5" maxlength="24" autocomplete="email" required /> </> ) }
다음과 같이, 전개 연산자(Spread operator, ...)를 사용해 나머지 매개변수(Rest parameters)로 폴스루 속성을 원하는 요소에 연결할 수 있습니다.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223export default function TextField({ label = '', hint = '', value, onChange, ...restProps }) { return ( <div style={{ marginBottom: '10px' }}> <label> {label && `${label}:`} <input {...restProps} value={value} onChange={e => onChange(e.target.value)} /> </label> {hint && ( <div style={{ marginTop: '4px', fontSize: '11px' }}> {hint} </div> )} </div> ) }
# 슬롯
컴포넌트의 템플릿 특정 위치에 다른 컴포넌트나 요소를 삽입할 수 있는 기능을 슬롯(Slot)이라고 합니다.children이라는 약속된 Prop을 사용해 슬롯을 구현할 수 있습니다.
123456789export default function Button({ children, loading = false, ...restProps }) { return ( <button className={loading ? 'loading' : ''} {...restProps}> {children} </button> ) }
123456789101112import { useState } from 'react' import Button from '@/components/Button' export default function App() { const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false) return ( <> <Button>취소</Button> <Button loading={loading}>확인</Button> </> ) }
# CSS 모듈(module)
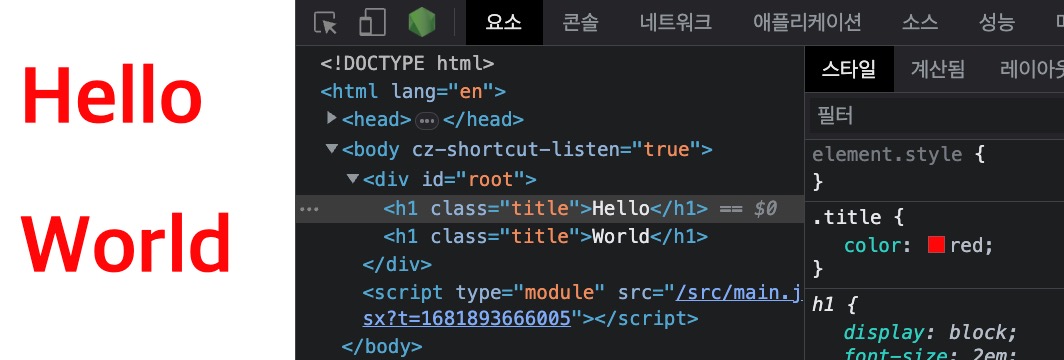
특정 컴포넌트의 스타일을 개별적인 CSS 파일로 만들어 연결할 수 있지만, 기본적으로는 모듈이 아니기 때문에 전역으로 적용되어, 선택자만 일치하면 의도치 않게 엉뚱한 다른 컴포넌트 요소에 스타일이 적용될 수도 있습니다.
다음 예제는 Hello.jsx를 위해 작성한 스타일(Hello.css)이 World.jsx에도 적용되는 것을 보여줍니다.
12345import './Hello.css' export default function Hello() { return <h1 className="title">Hello</h1> }
123.title { color: red; }
1234export default function Hello() { // 빨간색 글자 색상이 적용됨! return <h1 className="title">World</h1> }
1234567891011import Hello from '~/components/Hello' import World from '~/components/World' export default function App() { return ( <> <Hello /> <World /> </> ) }
 zoom_out_map
zoom_out_map
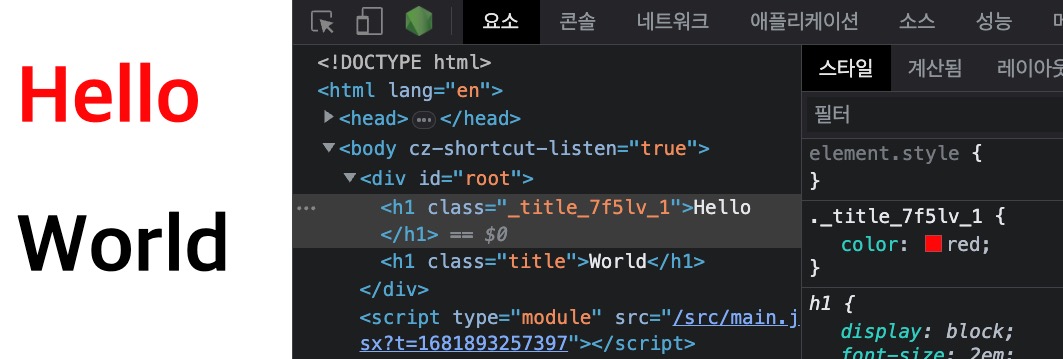
React에서는 효율적으로 스타일을 관리하기 위해, 각 컴포넌트에만 개별적으로 대응하는 스타일을 만들 수 있습니다.Hello.css 파일 이름을 Hello.module.css로 수정하면, 특정 컴포넌트에서만 유효한(Scoped) 스타일을 작성할 수 있습니다.
12345import styles from './Hello.module.css' export default function Hello() { return <h1 className={styles.title}>Hello</h1> }
123.title { color: red; }
 zoom_out_map
zoom_out_map
# SCSS 구성
Vite 프로젝트는 sass 패키지만 설치하면, 별도 구성 없이도 바로 Sass 혹은 SCSS를 사용할 수 있습니다.
특히 SCSS 중첩(Nesting) 문법을 사용하면, 훨씬 유연하게 스타일을 관리할 수 있습니다.
1npm i -D sass
1234567891011121314import styles from './Hello.module.scss' export default function Hello({ message = '' }) { return ( <> <h1 className={styles.title}> <span>Hello</span> Component~ </h1> <p className={styles.message}> {message} </p> </> ) }
1234567891011.title { font-size: 40px; span { font-weight: bold; color: royalblue; } } .message { font-size: 20px; opacity: .7; }
# 전역 스타일
만약 모듈 안에서 일부 전역 스타일을 적용하고 싶다면, 다음과 같이 :global 선택자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
1234567891011.title { font-size: 40px; span { font-weight: bold; color: royalblue; } } :global .message { font-size: 20px; opacity: .7; }
끝까지 읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
좋아요와 응원 댓글은 블로그 운영에 큰 힘이 됩니다!